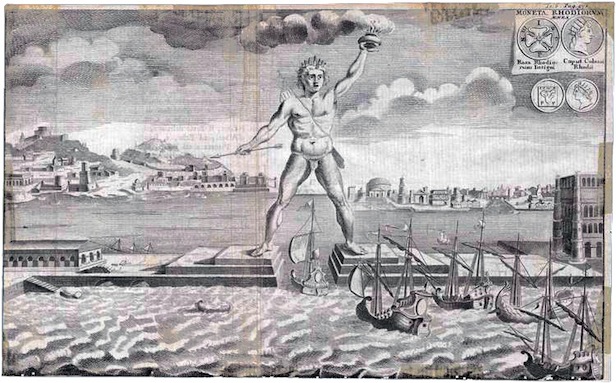
Over the ages, many people have attempted lists of the Seven Wonders of the World, however the original referred to architectural achievements of classic antiquity. The ancient wonders were the Great Pyramid of Giza; the Hanging Gardens of Babylon; the Statue of Zeus at Olympia; Temple of Artemis at Ephesus; Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, in modern Turkey; the Lighthouse of Alexandria; and the 30 metre high Colossus of Rhodes statue.
Over the ages, many people have attempted lists of the Seven Wonders of the World, however the original referred to architectural achievements of classic antiquity. The ancient wonders were the Great Pyramid of Giza; the Hanging Gardens of Babylon; the Statue of Zeus at Olympia; Temple of Artemis at Ephesus; Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, in modern Turkey; the Lighthouse of Alexandria; and the 30 metre high Colossus of Rhodes statue.
Of the seven, only the Great Pyramid of Giza remains, the rest were destroyed by earthquakes or were burnt down by later empires. Great scholars like the Greek historian Herodotus and the architect Callimachus of Cyrene both wrote lists of the Seven Wonders of the World, which were housed in the Museum of Alexandria and subsequently lost, but, for the Greeks, the Seven Wonders were not a high-minded pursuit. Instead of ‘wonders,’ the ancient Greeks spoke of ‘theamata,’ meaning ‘sights,’ as in ‘sight-seeing.’
The list of the Seven Wonders of the World was essentially a travel guide for tourists, in particular those of the first and second centuries BC, following the Greek conquest of much of the known world in the fourth century giving Greek travellers access to the civilisations of the Egyptians, Persians and Babylonians.